Table of Contents
Eliza- 1966

The grandmother of chatbots, Eliza, was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, at MIT in 1966. Eliza was one of the first chatbots designed to mimic a psychotherapist. She used simple pattern-matching techniques to make patients feel understood, even though she didn’t grasp the conversations.
Parry & Racter -1972 & 1984

Parry was created at Stanford University in 1972 by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby. Parry simulated a patient with schizophrenia, showcasing more advanced thinking than Eliza and demonstrating the potential of chatbots in psychiatry. Parry used a more advanced set of rules to mimic the thinking of a paranoid person. This helped it have more complex conversations based on the context and paved the way for more advanced chatbots.
In 1984, Racter (Raconteur) was one of the early attempts at creating a chatbot that could produce human-like text. Developed by William Chamberlain and Thomas Etter, Racter was not a fully interactive chatbot like modern ones but a text generator. It used a set of pre-programmed grammar rules to create seemingly coherent sentences and paragraphs, often in the form of surreal or absurd poetry. Racter wrote one masterpiece: “Policemen’s Beard is Half Constructed.”
Jabberwacky -1988
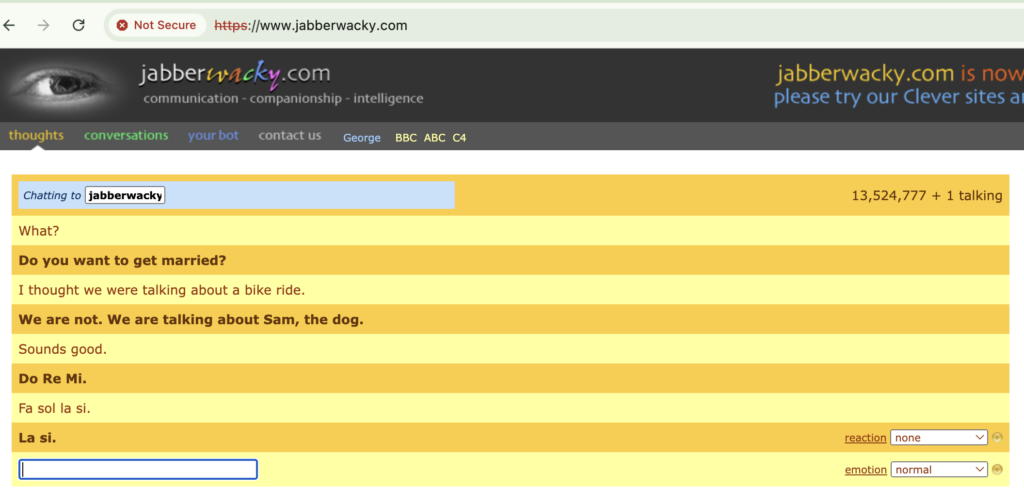
British programmer Rollo Carpenter created Jabberwacky in 1988. Jaberwacky’s purpose was to portray messages more entertainingly through artificial human conversations. In contrast to Parry or ELIZA, which were more rule-bound, Jabberwacky had a different style and did not follow any stiff rules but kept records of conversations and used them to produce responses.
Dr. Sbaitso -1992
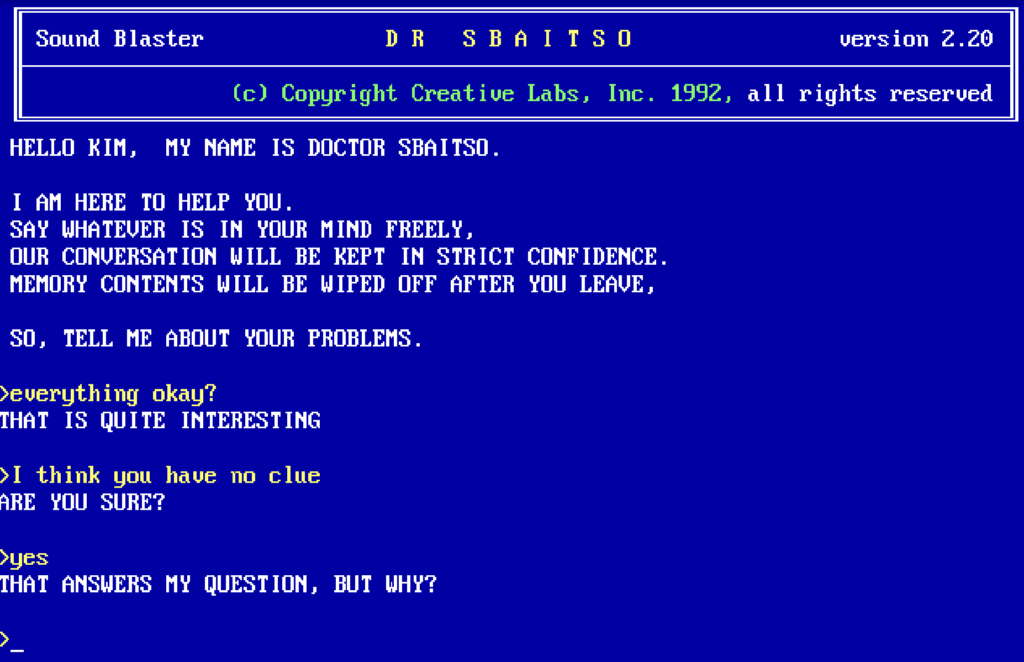
Presented by Creative Labs in 1992, Dr. Sbaitso was another primitive chatbot application that pretended to be a psychologist and worked on MS-DOS. Although its functionality was essential, it was revolutionary at the time.
ALICE -1995
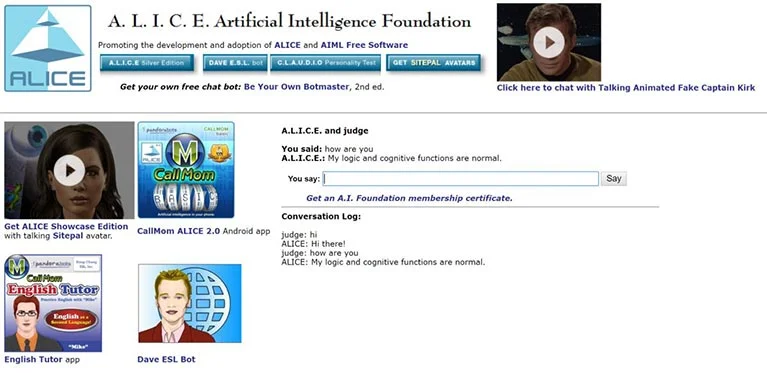
Dr. Richard Wallace created A.L.I.C.E. (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity) in 1995. Using her unique language, A.I.M.L. (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language), she won the Loebner Prize in Artificial Intelligence three times.
SmarterChild -2001

SmarterChild, developed by ActiveBuddy, became one of the first widely used chatbots on instant messaging platforms like AIM and MSN Messenger. Launched in 2001, it provided users with quick answers to questions, played games, and engaged in casual conversation. SmarterChild’s widespread use marked the beginning of integrating chatbots into consumer-facing platforms, setting the stage for today’s virtual assistants.
Siri -2011
In 2011, Apple introduced Siri, the first voice-activated virtual assistant. Siri revolutionized the way users interacted with their devices by allowing them to perform tasks, ask questions, and receive answers through natural language voice commands. Siri’s success paved the way for other voice-activated assistants, transforming the chatbot landscape from text-based interactions to voice-driven experiences.

Amazon Alexa -2014

Introduced by Amazon in 2014, Alexa became a household name as the voice behind Amazon’s Echo smart speakers. Alexa’s ability to control smart home devices, provide information, and perform various tasks made it one of the most popular virtual assistants in the market. Alexa’s integration with third-party services and skills extended its functionality, making it a versatile tool in the growing ecosystem of IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
Google Assistant -2016
Google Assistant, launched in 2016, further advanced the capabilities of virtual assistants by offering more conversational and context-aware interactions. Integrated across a range of Google products and smart devices, Google Assistant became a central part of Google’s ecosystem, allowing users to manage tasks, control smart home devices, and retrieve information seamlessly. Its use of advanced AI and machine learning set new standards for virtual assistants.